This report was published by the Kansas Supreme Court following a rigorous assessment of Kansas municipal court practices. It advances 18 recommendations for judges and courts to more fairly and constitutionally impose and enforce fines and fees and outlines an implementation plan for reform.
You can read the full text of the report here.
Recommendations
- Municipal and district judges should be allowed to reduce fines for defendants who are unable to pay the mandatory minimum.
- Before suspending a driver’s license for nonpayment of fines and fees, courts should hold an ability to pay hearing. Judges should be able to allow defendants to do community service to satisfy their outstanding debt. Reinstatement fees should be reduced or waived depending on the defendant’s ability to pay.
- Defendants should be given more credit against their debt for community service, and courts should consider additional alternatives to fines and fees
- “Municipalities should be encouraged to make their fines and court costs more uniform for traffic infractions and low-level misdemeanors.”
- To determine ability to pay, defendants should fill out an “affidavit of indigency,” or a form that explains their finances to the court.
- Courts should implement procedural protections (i.e. an ability to pay hearing and other due process protections) before revoking probation or parole due to nonpayment of fines and fees.
- “Municipal courts should establish guidelines for closing cases and writing off fines and fees for traffic offenses and misdemeanors after a reasonable time if collection efforts have not been successful.”
- “Convenient payment options should be offered, including payment by credit card in person, by telephone, or online, as well as other after-hour payment options.”
- The state of Kansas should “compile and distribute” information for municipal judges about the techniques that municipalities use to collect fines and fees, including payment plans and collections systems.
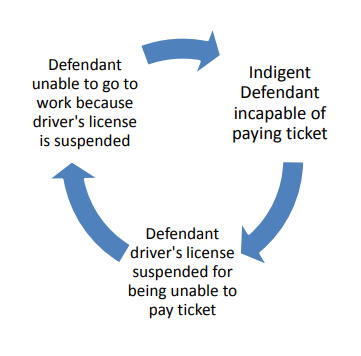
“Unfortunately, [driver’s license suspension] is also very effective in trapping indigent defendants in a vicious cycle. It begins with the defendant being indigent and therefore incapable of paying the fine. The defendant’s driver’s license is then suspended for failing to pay the fine. The defendant is unable to travel to work because of the suspended driver’s license and is still incapable of paying the fine.”